NOVEL APPROACHES TO LUNG CANCER PREVENTION: MODULATING EGFR PATHWAY WITH NATURAL COMPOUNDS
ABSTRACT
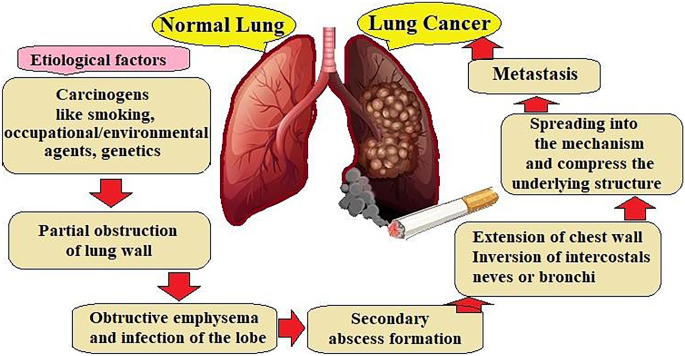
According to the World Health Organization(WHO), lung
carcinoma is the most common cause of cancer-related death in both developed
and developing countries. It
can generally be divided into two subtypes: Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)
accounting approximately 85% in all tumor cases, and Small cell lung
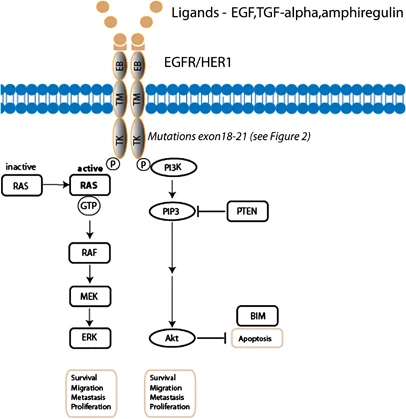
cancer(SCLC) . Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor(EGFR), a protein present on the
surface of cells and are crucial for Cell growth, proliferation, survival and
differentiation. It is a receptor Tyrosine Kinase when gets muted lead to
abnormal signaling that result in uncontrolled cell growth, proliferation and
necrosis. EGFR mutation prevalence appears to be consistent
across all stages of NSCLC.
Due to the severe side effects and acquiring multi-resistance, its clinical
treatment has always been difficult. Clinical efficiency of EGFR
inhibitors as gefitinib, afatinib, and Osimertinib is often limited by
resistance and show several side effects like diarrhoea, hepatotoxicity, skin
disorders, stomatitis etc.Natural
Compounds offer potential solutions by means of multi-targeting, fewer side
effects, and considerable therapeutic benefits. Integration of natural
compounds with conventional medicines shows higher response rate, superior
disease control, and better survival than in EGFR inhibitor mono-therapy.
Phytochemicals like polyphenols, saponins, terpenoids etc, derived from natural
sources are known to overcome resistance to EGFR inhibitors and improve their
therapeutic efficacy. Further exploration of these natural compounds may
be able to circumvent several pitfalls that exist with these treatments and
possibly offer superior results in the treatment of lung cancer.
Key
Words: Lung Cancer,
EGFR pathway, NSCLC, Phytochemicals.
INTRODUCTION
Cancer
treatment strategies have increasingly focused on targeting specific molecular
pathways, with the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) pathway emerging as
a critical target due to its role in cell growth and survival. Mutations in
EGFR are associated with several cancers, including non-small cell lung cancer
(NSCLC). Although conventional EGFR inhibitors like gefitinib and osimertinib
have shown initial success, their long-term effectiveness is often limited by
drug resistance and side effects. In recent years, natural compounds derived
from plants and other natural sources have gained attention as promising
alternatives. These compounds, including polyphenols, terpenoids, and saponins,
exhibit multi-targeting properties and reduced toxicity. Modulating EGFR
pathways with natural compounds offers a novel approach to cancer treatment,
potentially improving therapeutic efficacy and overcoming the limitations of
traditional therapies. This emerging field provides hope for developing more
effective and less toxic cancer treatments through the integration of
nature-based compounds.
TYPES OF LUNG CANCER
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF LUNG CANCER
WHAT IS EGFR?
In
conclusion, lung carcinoma remains a leading cause of cancer-related deaths
worldwide, with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) being the most prevalent
subtype. The role of EGFR mutations in driving tumor growth highlights the need
for targeted therapies. However, the clinical use of EGFR inhibitors is often
hindered by resistance and significant side effects. Natural compounds, with
their multi-targeting abilities and reduced toxicity, offer promising adjuncts
to conventional treatments. Combining phytochemicals with EGFR inhibitors may
enhance therapeutic outcomes, overcome drug resistance, and provide more
effective and safer treatment strategies for lung cancer. Further research in
this area could lead to improved clinical approaches and patient survival.





Comments
Post a Comment